Gradient Descent Method Example#
Import the required libraries#
import pepflow as pf
import numpy as np
import sympy as sp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import itertools
from IPython.display import display
Define the functions#
L = pf.Parameter("L")
f = pf.SmoothConvexFunction(is_basis=True, tags=["f"], L=L)
Write a function to return the PEPContext associated with GD#
def make_ctx_gd(
ctx_name: str, N: int | sp.Integer, stepsize: pf.Parameter
) -> pf.PEPContext:
ctx_gd = pf.PEPContext(ctx_name).set_as_current()
x = pf.Vector(is_basis=True, tags=["x_0"])
f.set_stationary_point("x_star")
for i in range(N):
x = x - 1 / L * f.grad(x)
x.add_tag(f"x_{i + 1}")
return ctx_gd
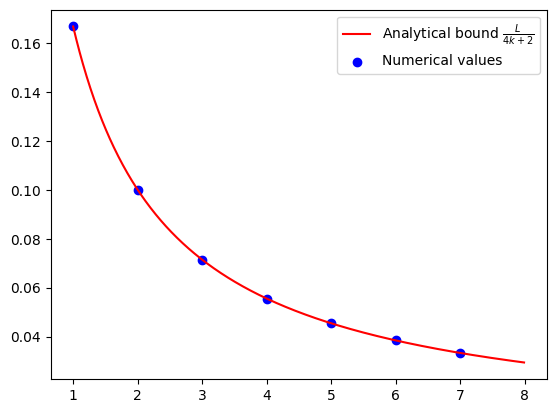
Numerical evidence of convergence of GD#
N = 8
R = pf.Parameter("R")
L_value = 1
R_value = 1
ctx_plt = make_ctx_gd(ctx_name="ctx_plt", N=N, stepsize=1 / L)
pb_plt = pf.PEPBuilder(ctx_plt)
pb_plt.add_initial_constraint(
((ctx_plt["x_0"] - ctx_plt["x_star"]) ** 2).le(R, name="initial_condition")
)
opt_values = []
for k in range(1, N):
x_k = ctx_plt[f"x_{k}"]
pb_plt.set_performance_metric(f(x_k) - f(ctx_plt["x_star"]))
result = pb_plt.solve(resolve_parameters={"L": L_value, "R": R_value})
opt_values.append(result.opt_value)
iters = np.arange(1, N)
cont_iters = np.arange(1, N, 0.01)
plt.plot(
cont_iters,
L_value / (4 * cont_iters + 2),
"r-",
label="Analytical bound $\\frac{L}{4k + 2}$",
)
plt.scatter(iters, opt_values, color="blue", marker="o", label="Numerical values")
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7fb6fb41c8d0>
Verification of convergence of GM#
N = sp.S(2)
L_value = sp.S(1)
R_value = sp.S(1)
ctx_prf = make_ctx_gd(ctx_name="ctx_prf", N=N, stepsize=1 / L)
pb_prf = pf.PEPBuilder(ctx_prf)
pb_prf.add_initial_constraint(
((ctx_prf["x_0"] - ctx_prf["x_star"]) ** 2).le(R, name="initial_condition")
)
pb_prf.set_performance_metric(f(ctx_prf[f"x_{N}"]) - f(ctx_prf["x_star"]))
result = pb_prf.solve(resolve_parameters={"L": L_value, "R": R_value})
print(result.opt_value)
# Dual variables associated with the interpolations conditions of f with no relaxation
lamb_dense = result.get_scalar_constraint_dual_value_in_numpy(f)
0.09999778825848643
pf.launch_primal_interactive(
pb_prf, ctx_prf, resolve_parameters={"L": L_value, "R": R_value}
)
Dash app running on http://127.0.0.1:8050/
Solve the problem again with the found relaxation#
def tag_to_index(tag, N=N):
"""This is a function that takes in a tag of an iterate and returns its index.
We index "x_star" as "N+1 where N is the last iterate.
"""
# Split the string on "_" and get the index
if (idx := tag.split("_")[1]).isdigit():
return int(idx)
elif idx == "star":
return N + 1
relaxed_constraints = []
for tag_i in lamb_dense.row_names:
i = tag_to_index(tag_i)
if i == N + 1:
continue
for tag_j in lamb_dense.col_names:
j = tag_to_index(tag_j)
if i < N and i + 1 == j:
continue
relaxed_constraints.append(f"f:{tag_i},{tag_j}")
pb_prf.set_relaxed_constraints(relaxed_constraints)
Solve the PEP problem again with the relaxed constraints and store the results.
result = pb_prf.solve(resolve_parameters={"L": L_value, "R": R_value})
# Dual variable associated with the initial condition
tau_sol = result.dual_var_manager.dual_value("initial_condition")
# Dual variable associated with the interpolations conditions of f
lamb_sol = result.get_scalar_constraint_dual_value_in_numpy(f)
# Dual variable associated with the Gram matrix G
S_sol = result.get_gram_dual_matrix()
Verify closed form expression of \(\lambda\)#
Print the values of \(\lambda\) obtained from the solver
lamb_sol.pprint()
\[\begin{split}\displaystyle \displaystyle
\begin{array}{c|cccc}
& x_0 & x_1 & x_2 & x_\star \\
\hline
x_0 & 0.0 & 0.25 & 0.0 & 0.0 \\x_1 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.667 & 0.0 \\x_2 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 \\x_\star & 0.25 & 0.417 & 0.333 & 0.0 \\
\end{array}
\end{split}\]
def lamb(tag_i, tag_j, N=N):
i = tag_to_index(tag_i)
j = tag_to_index(tag_j)
if i == N + 1: # Additional constraint 1 (between x_★)
if j == 0:
return lamb("x_0", "x_1")
elif j < N:
return lamb(f"x_{j}", f"x_{j + 1}") - lamb(f"x_{j - 1}", f"x_{j}")
elif j == N:
return 1 - lamb(f"x_{N - 1}", f"x_{N}")
if i < N and i + 1 == j: # Additional constraint 2 (consecutive)
return j / (2 * N + 1 - j)
return 0
lamb_cand = pf.pprint_labeled_matrix(
lamb, lamb_sol.row_names, lamb_sol.col_names, return_matrix=True
)
\[\begin{split}\displaystyle \displaystyle
\begin{array}{c|cccc}
& x_0 & x_1 & x_2 & x_\star \\
\hline
x_0 & 0.0 & 0.25 & 0.0 & 0.0 \\x_1 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.667 & 0.0 \\x_2 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 \\x_\star & 0.25 & 0.417 & 0.333 & 0.0 \\
\end{array}
\end{split}\]
Check whether our candidate of \(\lambda\) matches with solution
print(
"Did we guess the right closed form of lambda?",
np.allclose(lamb_cand, lamb_sol.matrix, atol=1e-4),
)
Did we guess the right closed form of lambda? True
Verify closed form expression \(S\)#
Create an ExpressionManager to translate \(x_i\), \(f(x_i)\), and \(\nabla f(x_i)\) into a basis representation
pm = pf.ExpressionManager(ctx_prf, resolve_parameters={"L": L_value, "R": R_value})
Print the values of \(S\) obtained from the solver
S_sol.pprint()
\[\begin{split}\displaystyle \displaystyle
\begin{array}{c|ccccc}
& x_0 & x_\star & \nabla f(x_0) & \nabla f(x_1) & \nabla f(x_2) \\
\hline
x_0 & 0.1 & -0.1 & -0.125 & -0.208 & -0.167 \\x_\star & -0.1 & 0.1 & 0.125 & 0.208 & 0.167 \\\nabla f(x_0) & -0.125 & 0.125 & 0.25 & 0.208 & 0.167 \\\nabla f(x_1) & -0.208 & 0.208 & 0.208 & 0.667 & 0.167 \\\nabla f(x_2) & -0.167 & 0.167 & 0.167 & 0.167 & 0.5 \\
\end{array}
\end{split}\]
Subtract the decomposed closed-form expressions
x = ctx_prf.tracked_point(f)
x_0 = ctx_prf["x_0"]
x_star = ctx_prf["x_star"]
tau_cand = L / sp.S(4 * N + 2)
grad_terms = sum(lamb(x_star.tag, x[i].tag) * f.grad(x[i]) for i in range(N + 1))
z_N = x_star - x_0 + 1 / (2 * tau_cand) * grad_terms
iter_diff_square = tau_cand * z_N**2
remainder_1 = S_sol.matrix - pm.eval_scalar(iter_diff_square).inner_prod_coords
pf.pprint_labeled_matrix(remainder_1, S_sol.row_names, S_sol.col_names)
\[\begin{split}\displaystyle \displaystyle
\begin{array}{c|ccccc}
& x_0 & x_\star & \nabla f(x_0) & \nabla f(x_1) & \nabla f(x_2) \\
\hline
x_0 & 0.0 & -0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & -0.0 \\x_\star & -0.0 & 0.0 & -0.0 & -0.0 & 0.0 \\\nabla f(x_0) & 0.0 & -0.0 & 0.094 & -0.052 & -0.042 \\\nabla f(x_1) & 0.0 & -0.0 & -0.052 & 0.233 & -0.181 \\\nabla f(x_2) & -0.0 & 0.0 & -0.042 & -0.181 & 0.222 \\
\end{array}
\end{split}\]
grad_diff_square = pf.Scalar.zero()
for i in range(N + 1):
for j in range(i + 1, N + 1):
const_1 = (2 * N + 1) * lamb(x_star.tag, x[i].tag) - 1
const_2 = lamb(x_star.tag, x[j].tag)
grad_diff_square += (
1 / (2 * L) * (const_1 * const_2 * (f.grad(x[i]) - f.grad(x[j])) ** 2)
)
remainder_2 = remainder_1 - pm.eval_scalar(grad_diff_square).inner_prod_coords
pf.pprint_labeled_matrix(remainder_2, S_sol.row_names, S_sol.col_names)
\[\begin{split}\displaystyle \displaystyle
\begin{array}{c|ccccc}
& x_0 & x_\star & \nabla f(x_0) & \nabla f(x_1) & \nabla f(x_2) \\
\hline
x_0 & 0.0 & -0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & -0.0 \\x_\star & -0.0 & 0.0 & -0.0 & -0.0 & 0.0 \\\nabla f(x_0) & 0.0 & -0.0 & -0.0 & -0.0 & 0.0 \\\nabla f(x_1) & 0.0 & -0.0 & -0.0 & -0.0 & 0.0 \\\nabla f(x_2) & -0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & 0.0 & -0.0 \\
\end{array}
\end{split}\]
S_guess = iter_diff_square + grad_diff_square
S_guess_eval = pm.eval_scalar(S_guess).inner_prod_coords
pf.pprint_labeled_matrix(S_guess_eval, S_sol.row_names, S_sol.col_names)
\[\begin{split}\displaystyle \displaystyle
\begin{array}{c|ccccc}
& x_0 & x_\star & \nabla f(x_0) & \nabla f(x_1) & \nabla f(x_2) \\
\hline
x_0 & 0.1 & -0.1 & -0.125 & -0.208 & -0.167 \\x_\star & -0.1 & 0.1 & 0.125 & 0.208 & 0.167 \\\nabla f(x_0) & -0.125 & 0.125 & 0.25 & 0.208 & 0.167 \\\nabla f(x_1) & -0.208 & 0.208 & 0.208 & 0.667 & 0.167 \\\nabla f(x_2) & -0.167 & 0.167 & 0.167 & 0.167 & 0.5 \\
\end{array}
\end{split}\]
Check whether our candidate of \(S\) matches with solution
print(
"Did we guess the right closed form of S?",
np.allclose(pm.eval_scalar(S_guess).inner_prod_coords, S_sol.matrix, atol=1e-4),
)
Did we guess the right closed form of S? True
Symbolic calculation#
Assemble the RHS of the proof.
interp_scalar_sum = pf.Scalar.zero()
for x_i, x_j in itertools.product(x, x):
if lamb(x_i.tag, x_j.tag) != 0:
interp_scalar_sum += lamb(x_i.tag, x_j.tag) * f.interp_ineq(x_i.tag, x_j.tag)
display(interp_scalar_sum)
\[\displaystyle 0+1/4*(f(x_1)-f(x_0)+\nabla f(x_1)*(x_0-(x_1))+1/2*L*\|\nabla f(x_0)-\nabla f(x_1)\|^2)+2/3*(f(x_2)-f(x_1)+\nabla f(x_2)*(x_1-(x_2))+1/2*L*\|\nabla f(x_1)-\nabla f(x_2)\|^2)+1/4*(f(x_0)-f(x_\star)+\nabla f(x_0)*(x_\star-x_0)+1/2*L*\|\nabla f(x_\star)-\nabla f(x_0)\|^2)+5/12*(f(x_1)-f(x_\star)+\nabla f(x_1)*(x_\star-(x_1))+1/2*L*\|\nabla f(x_\star)-\nabla f(x_1)\|^2)+1/3*(f(x_2)-f(x_\star)+\nabla f(x_2)*(x_\star-(x_2))+1/2*L*\|\nabla f(x_\star)-\nabla f(x_2)\|^2)\]
RHS = interp_scalar_sum - S_guess
display(RHS)
\[\displaystyle 0+1/4*(f(x_1)-f(x_0)+\nabla f(x_1)*(x_0-(x_1))+1/2*L*\|\nabla f(x_0)-\nabla f(x_1)\|^2)+2/3*(f(x_2)-f(x_1)+\nabla f(x_2)*(x_1-(x_2))+1/2*L*\|\nabla f(x_1)-\nabla f(x_2)\|^2)+1/4*(f(x_0)-f(x_\star)+\nabla f(x_0)*(x_\star-x_0)+1/2*L*\|\nabla f(x_\star)-\nabla f(x_0)\|^2)+5/12*(f(x_1)-f(x_\star)+\nabla f(x_1)*(x_\star-(x_1))+1/2*L*\|\nabla f(x_\star)-\nabla f(x_1)\|^2)+1/3*(f(x_2)-f(x_\star)+\nabla f(x_2)*(x_\star-(x_2))+1/2*L*\|\nabla f(x_\star)-\nabla f(x_2)\|^2)-(L/10*\|x_\star-x_0+1/2*L/10*(1/4*\nabla f(x_0)+5/12*\nabla f(x_1)+1/3*\nabla f(x_2))\|^2+0+1/2*L*5/48*\|\nabla f(x_0)-\nabla f(x_1)\|^2+1/2*L*1/12*\|\nabla f(x_0)-\nabla f(x_2)\|^2+1/2*L*13/36*\|\nabla f(x_1)-\nabla f(x_2)\|^2)\]
Assemble the LHS of the proof
LHS = f(x[N]) - f(x_star) - L / (4 * N + 2) * (x[0] - x_star) ** 2
display(LHS)
\[\displaystyle f(x_2)-f(x_\star)-L/10*\|x_0-x_\star\|^2\]
diff = LHS - RHS
display(diff)
\[\displaystyle f(x_2)-f(x_\star)-L/10*\|x_0-x_\star\|^2-(0+1/4*(f(x_1)-f(x_0)+\nabla f(x_1)*(x_0-(x_1))+1/2*L*\|\nabla f(x_0)-\nabla f(x_1)\|^2)+2/3*(f(x_2)-f(x_1)+\nabla f(x_2)*(x_1-(x_2))+1/2*L*\|\nabla f(x_1)-\nabla f(x_2)\|^2)+1/4*(f(x_0)-f(x_\star)+\nabla f(x_0)*(x_\star-x_0)+1/2*L*\|\nabla f(x_\star)-\nabla f(x_0)\|^2)+5/12*(f(x_1)-f(x_\star)+\nabla f(x_1)*(x_\star-(x_1))+1/2*L*\|\nabla f(x_\star)-\nabla f(x_1)\|^2)+1/3*(f(x_2)-f(x_\star)+\nabla f(x_2)*(x_\star-(x_2))+1/2*L*\|\nabla f(x_\star)-\nabla f(x_2)\|^2)-(L/10*\|x_\star-x_0+1/2*L/10*(1/4*\nabla f(x_0)+5/12*\nabla f(x_1)+1/3*\nabla f(x_2))\|^2+0+1/2*L*5/48*\|\nabla f(x_0)-\nabla f(x_1)\|^2+1/2*L*1/12*\|\nabla f(x_0)-\nabla f(x_2)\|^2+1/2*L*13/36*\|\nabla f(x_1)-\nabla f(x_2)\|^2))\]
pf.pprint_str(
diff.repr_by_basis(ctx_prf, sympy_mode=True, resolve_parameters={"L": sp.S("L")})
)
\[\displaystyle \displaystyle 0\]
With verified closed form expression, we have verified the below for fixed \(N\)#
\[\begin{align*}
&f(x_N) - f(x_\star) - \frac{L}{4N+2} \| x_0 - x_\star \|^2 \\
&= \sum _{i=1}^N \lambda_{i,i-1} \left( f(x_{i})-f(x_{i-1}) + \langle \nabla f(x_{i}) , x_{i-1} - x_{i} \rangle + \frac{1}{2 L} \| \nabla f(x_{i-1}) - \nabla f(x_i) \|^2 \right) \\
&\quad +\sum _{i=0}^N \lambda_{\star,i} \left( f(x_i)-f(x_{\star}) + \langle \nabla f(x_{i}) , x_{\star} - x_{i} \rangle + \frac{1}{2 L} \| \nabla f(x_i) \|^2 \right) \\
&\quad - \frac{1}{2L} \sum_{i=0}^N \sum_{j=i+1}^N \lambda_{\star,j} \left( (2N+1) \lambda_{\star,i} - 1 \right) \| \nabla f(x_j) -\nabla f(x_i) \|^2 \\
&\quad- \frac{L}{4N+2} \left\| x_0 - \frac{2N+1}{L} \sum_{i=0}^{N} \lambda_{\star,i} \nabla f(x_i) - x_\star \right\|^2
\end{align*}\]
where
\[\begin{align*}
\lambda_{i-1,i} = \frac{i}{2N + 1 - i}, \quad i = 1, \dots, N,
\qquad
\lambda_{\star,i} =
\begin{cases}
\lambda_{0,1} & i = 0 \\
\lambda_{i,i+1} - \lambda_{i-1,i} & i = 1, \dots, N-1 \\
1 - \lambda_{i-1,i} & i = N
\end{cases}
\end{align*}\]